Scientists find evidence supporting temperate niche conservatism hypothesis in liverworts
Published 12 October, 2024
Phylogenetic niche conservatism posits that species tend to retain ancestral ecological traits and distributions, which has been broadly tested for lineages originating in tropical climates. In lineages that originated and diversified in temperate climates, such studies have rarely been conducted.
Liverworts are thought to originate in temperate climates, with the mean lineage age reflecting the evolutionary history of biological communities. In a new study by a team of researchers from China, Switzerland and the US, the age-component of the temperate niche conservatism hypothesis was tested in regional liverwort floras across a long latitudinal gradient from the tropical to arctic climates.
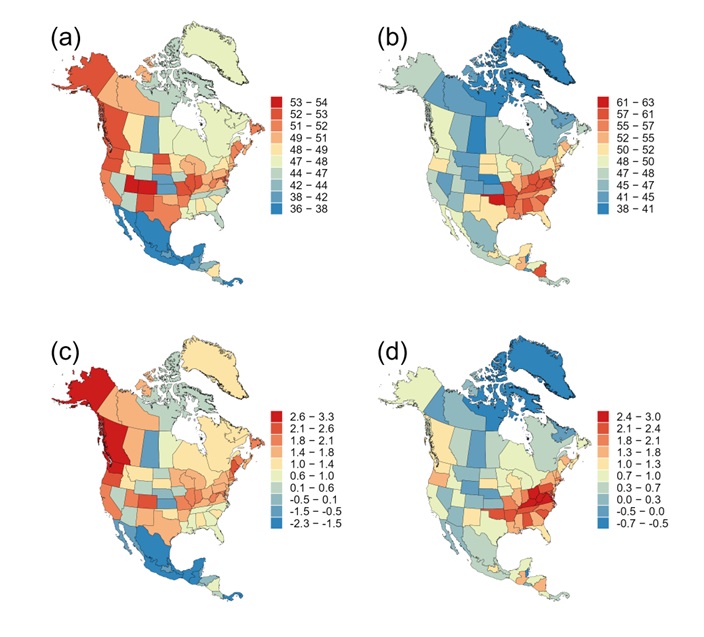
“We estimated the mean genus age (MGA) for each of 76 regional floras of liverworts, and related MGA to climatic variables for North America as a whole and for its eastern and western parts separately, and used variation partitioning analysis to assess the relative importance of temperature- versus precipitation-related variables and of climate extremes versus seasonality on MGA.,” explains Hong Qian, lead and corresponding author of the study, which is published in the KeAi journal Plant Diversity.
The researchers found that older genera of liverworts tend to concentrate in humid regions of intermediate temperatures in the range of 10-20 °C, from which liverworts have adapted to and diversified into more arid, colder, and hotter regions, supporting the temperate niche conservatism hypothesis.
“We also found that across North America the MGA of liverwort assemblages is more strongly affected by precipitation-related variables than by temperature-related variables, and by climate extremes than by climate seasonality,” adds Qian.
Geographic patterns of the MGA of liverworts revealed in this study are consistent with the temperate niche conservatism hypothesis, which accounts for the distributions of taxa in lineages that originated and diversified in temperate climates.
“This means that these patterns contradict the tropical niche conservatism hypothesis which is broadly supported by angiosperms,” says Qian.
Contact author: Hong Qian,hong.qian@illinoisstatemuseum.org
See the article: Qian et al., 2024, Geographic patterns and climatic drivers of the mean genus age of liverworts in North America. Plant Diversity , https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pld.2024.07.002